Welcome back to our RVI Insulation Education blog series!
In the first blog of this series, we discussed the foundational concept of insulation and its critical importance in homes. We covered how insulation slows heat transmission through a building’s floors, walls, and ceilings. This minimizes energy loss, improves comfort, and reduces heating and cooling equipment size. We also explored the structural benefits of proper insulation, such as noise reduction, enhanced fire resistance, and prevention of mold growth due to controlled airflow and moisture management.
By the end, as a reader, you understood the importance of insulation in creating a home’s thermal envelope, how it’s crucial for energy efficiency and long-term cost savings, and the added value and health benefits for homeowners.
In this second article of the series, we’ll delve into the science behind insulation, providing a deeper understanding of how it works and why it’s crucial for your home. We’ll cover key elements such as the thermal envelope, pressure boundary, moisture issues, and heat transfer. Each of these factors plays a vital role in making a house energy-efficient, comfortable, and safe!
What is the Thermal Envelope?
The “thermal envelope” is integral to a home’s insulation system. This term refers to the physical barrier that separates the interior living spaces from the external environment. This envelope mitigates heat transfer through various components of your home, including the walls, ceilings, floors, windows, doors, chimneys, and flue pipes.
By properly insulating these areas, you create a shield that minimizes the loss or gain of heat, ensuring the home maintains a consistent temperature.
This also has an impact on the house’s HVAC system. If the HVAC is correctly sized, but the insulation is installed poorly, the building will be uncomfortable and costly to heat and cool. However, an efficiently insulated thermal envelope directly influences the performance of the HVAC system. Proper insulation keeps a house’s interior climate controlled and reduces the need for excessive HVAC usage.
This all ties back to the First Law of Thermal Dynamics, which states: “Energy can be neither created nor destroyed in an isolated system; rather, it’s transformed or transferred from one form to another.”
Consider the Pressure Boundary
The next important concept is the “pressure boundary,” often called the “air barrier.” This is how we mitigate air leakage and manage moisture. Air leakage can account for 30% or more of a home’s heating and cooling costs. Leakage raises energy bills and brings in issues like unwanted moisture, noise, and dust, providing easy access to pollutants and insects.
Air sealing a house is vital for efficiency and health and should be sealed to meet the Air Sealing Home Performance with Energy Star® Seal of Approval. Effective air barriers ensure that the home maintains its integrity, preventing uncomfortable drafts and maintaining quality indoor air.


Mitigate Moisture to Prevent Major Issues
Moisture management is another critical component in a well-insulated home. Issues related to moisture, such as mold, are often a result of poor ventilation, improper air sealing, and inadequate insulation. Excess moisture can lead to mold growth, which poses serious health risks, including respiratory problems and allergies.
Another issue is dust mites, which thrive in moisture-rich environments. A basement with a moisture problem, when covered with carpet, can significantly increase the prevalence of dust mites and other allergens. Addressing moisture correctly from the start can prevent these issues and contribute to a healthier living environment.
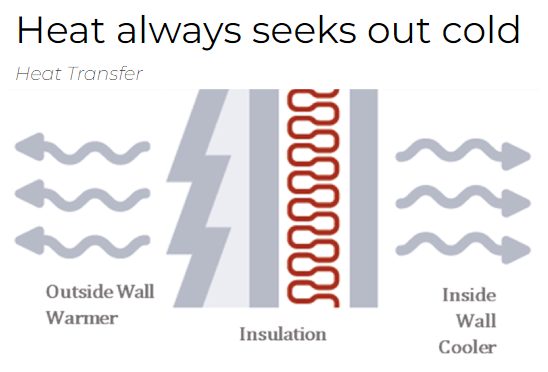
Understanding Heat Transfer
The fundamental principle to remember is that heat always seeks out cold. This natural process means that during winter, heat will attempt to escape your home, and during summer, heat will strive to invade your cool living space. Insulation acts as a barrier to this transfer, reducing the rate at which heat moves in or out of your home.
By halting unwanted heat transfer, you maintain a stable indoor climate, making heating and cooling systems more effective and cost-efficient.
What’s Next
Now that you have a basic understanding of the science behind insulation, you can make more confident decisions about building a more energy-efficient, comfortable, and healthy home. By focusing on the thermal envelope, pressure boundary, moisture management, and heat transfer, you can ensure that your insulation system functions optimally.
Stay tuned for the next installment in our series, where we’ll continue to explore these topics in greater detail, helping you master the art of insulation. We’ll be addressing how insulation needs to be addressed in Northern Wisconsin.



